Desperate and trapped, Gaza's youth turn to suicide
His death by suicide on 3 July sent shockwaves through the community – this was a man who led the 'We Want to Live' movement against poverty in March 2019, and fearlessly stood up to Hamas.
Many Palestinians felt that if he had reached a point where life was no longer worth living then there was little hope for other Gazans, who have been living under a crushing blockade for 14 years in what human rights groups describe as an open-air prison.
In a society where suicide is taboo, Al Ajuri's father Abu Muhammed spoke to BBC World News last week. "I don't really know what pushed my son to commit suicide. We were sitting together at home and we ate his last meal together," he said.
"There was no problem and I don't know yet what happened to him. I don't think poverty alone is a reason for suicide. We as a family, are still living in a state of great shock."
However, Suleiman's close friend Shaher Al Habbash was able to provide an insight into Suleiman's life and how he was feeling shortly before his death. Al Habbash told The National that Suleiman had been hoping to emigrate from Gaza but had been unable to collect the money to do so which had left him devastated.
 |
There have been 30 deaths and 600 attempted suicides in the first seven months of 2020 |  |
"Hamas' Internal Security Force arrested him several times. They attacked his family home and humiliated him during his interrogation inside Hamas prisons," he added. "They even raided the home during his sister's wedding. This bothered him a lot."
The 'We Want to Live' movement last year was viewed by Hamas as a threat and the protests were violently broken up. Suleiman was arrested for "spreading chaos." His friends attribute Hamas' ongoing harassment and the despair of realising there was no way out of Gaza as the factors that led to his death.
 |
|
| Read more: Mental health in Palestine among world's worst |
On the day that Suleiman died, another three young Gazans committed suicide. Ayman Al Ghoul, 24, threw himself off the 5th floor of a building in al-Shati refugee camp. A 30-year-old woman hung herself in Rafah, and Ibrahim Yassin, 21, a teacher employed by UNRWA, died from wounds sustained from setting himself on fire the previous week.
The day after Suleiman's death, Ahmed Al Malahi swallowed fifty pills, a young teenager attempted to throw herself off the balcony of her home, and an 18-year-old swallowed dozens of pills in an attempted suicide.
Another three days later, a young Gazan tried to jump off a balcony at the Ministry of Social Affairs when he was denied aid. And then, on 9 July, Eyas Shehada was arrested by Hamas for threatening to commit suicide if his problems were ignored. Eyas went from door to door asking Hamas officials for help while recording a Facebook Live, talking about his homelessness, destitution and inability to provide for his family.
Journalist Usama Al Kahlout was arrested by Hamas that day for covering Eyas' story. Al Mezan Centre for Human Rights reported that on the day of Suleiman's funeral, thirteen of his friends were arrested, nine at the cemetery and four at his house paying condolences. Two journalists reporting on his suicide were arrested that same day.
 |
The idea of committing suicide is on the mind of most young Gazans I know |  |
While authorities in Gaza do not keep an official toll of suicides, rights groups say there has been an alarming spike in deaths. The Palestinian Centre for Conflict Resolution has reported 30 deaths by suicide and 600 attempted suicides in the first seven months of 2020, a threefold increase in five years. In 2015, a total of 10 suicides were recorded in Gaza, according to statistics compiled by The New Arab's Arabic-language site
Hamas denies that the rate of deaths by suicide is increasing but has arrested journalists and activists who openly talk about it.
"The reasons for people dying by suicide in Gaza are the absence of hope that things will change for the better, the mental health pressures as a result of Israel's blockade on Gaza, as well as internal division and suppression of freedoms," Palestinian human rights defender and activist Issa Amro, who is based in the West Bank, told The New Arab.
"In an Arab and Islamic society death by suicide is not accepted. It is one of the major sins in Islam and is considered by society as something that brings shame on the person and their family," he added.
 |
|
| The UN describes Gaza as 'unliveable', with 80 percent of the population reliant on international aid. [Getty] |
Despite the strong social stigma, Gazan writer, analyst and manager at Euro-Med Monitor Muhammed Shehada says that nearly everyone he knows in Gaza has contemplated suicide at least once. "Generally, the idea of committing suicide is on the mind of most young Gazans I know as a result of being stuck in a state of non-life, of neither living nor dying for most of their adult lives," Shehada tells The New Arab.
"They feel that even their basic survival has become a burden on their families, a painful existence, and a matter shame, as most young Gazans see themselves approaching the age of 30 without a job, without savings, without being able to secure the minimum of a decent life or start a family of their own."
"The answer to this conundrum is usually to escape a sunken vessel. Whether through emigration and travel to the unknown, drugs that help one ignore his surroundings, or taking one's life."
The factors that have been attributed to Gaza's suicide crisis are numerous and multi-faceted. First there is the dire economic situation and high rates of unemployment as a result of both Israel and Egypt s' blockade on the Gaza Strip. The UN describes Gaza as "unliveable", with 80 percent of the population reliant on international aid, 69 percent living below the poverty line, a rate of 64 percent youth unemployment, and between two to four hours of running water and electricity a day.
 |
The reason for people dying by suicide in Gaza is the absence of hope that things will change for the better |  |
Before President Abdel-Fattah al-Sisi closed Egypt's border crossings and cracked down on Gaza's smuggling tunnels in 2014, there were still ways in which young Gazans could gather the money needed to acquire the required travel documents, cross the border into Egypt and then make their way to Turkey, with the hopes of finding opportunities there or further beyond in Europe. This is now impossible.
"The blockade imposed by Egypt is more severe than the blockade of Israel, as Egypt has, since Abdel Fattah al-Sisi assumed power, closed and destroyed tunnels and narrowed the world," Bassem Eid, a Palestinian human rights activist, journalist and political analyst based in Jerusalem, told The New Arab.
Eid explains that in addition to the blockade Gazans "face and are subject to…beatings, arrests, repression of freedoms, silencing of prisoners and torture in prisons from Hamas militants."
Then there is the lasting trauma and staggering rates of Gazans suffering from mental health conditions such as PTSD, anxiety disorders and clinical depression as a result of three major Israeli military operations since 2008, most notably the 50-day war in 2014 which killed over 2,200 Palestinians.
 |
|
| Mental health conditions such as PTSD, anxiety disorders and clinical depression are widespread in Gaza. [Getty] |
"Rocket fire from Gaza into Israel and the violent Israeli response have destroyed the rest of the Strip. Such wars burden the people, and the people of Gaza are no longer able to bear the burdens resulting from those wars. The people of Gaza dream about death more than they dream of living," says Eid.
Gaza's healthcare sector is overwhelmed and priority is given to those with physical injuries, such as the thousands that were shot and wounded by Israeli forces during the Great March of Return last year, in addition to injuries from rocket fire between both sides and excessive use of force by Israeli forces at the borders.
Those with mental health illnesses come second. It doesn't help that US President Donald Trump cut $90 million from the UN's aid budget to Gaza in 2018, which has left UNRWA's mental health unit in Gaza with a £315 million funding deficit.
Against all odds, the Gaza Community Mental Health Programme (GCMHP) does its best to provide mental and psychological health support to the local population, as does Sumud Palestine, a charity based in the UK that sends mental health professionals to volunteer in Gaza. But with a heavily traumatised population of two million people, including 400,000 children that UNICEF says are in need of psychological support, they can't reach everybody.
 |
Most young Gazans see themselves approaching the age of 30 without a job, without savings, without being able to secure the minimum of a decent life or start a family of their own |  |
"There's little that psychologists can fix. Rehabilitation and psychological treatment are meant to help individuals to reintegrate into society and return to a normal life, but in Gaza there's no life in the first place, the siege psychologically and emotionally suffocates life out of the enclave," says Shehada from Euro-Med Monitor.
"Furthermore, an Israeli Arab psychologist, Mohammed Mansour, who travelled to Gaza in late 2017 noted that even Gazan psychologists themselves were suffering from depression, anxiety and despair, the very issues they are supposed to treat amongst the population."
The Covid-19 pandemic has also played a role in the recent spike in suicides in Gaza over the past four weeks. Travel restrictions from Egypt and Israel to control the pandemic, plus Israel's recent annexation plans, have resulted in the Palestinian Authority ceasing all coordination with Israel, making leaving Gaza virtually impossible.
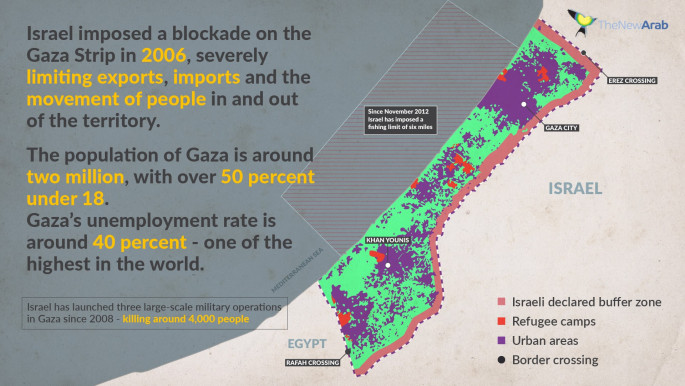 |
|
| Click to enlarge |
Since the outbreak of Covid-19, 4,000 Gazans have lost their jobs and 50 factories have closed their doors forever. New pressures such as extreme overcrowding in the home - with children unable to attend school and men unemployed - has also resulted in increased rates of domestic violence.
The Gaza Community Mental Health Programme (GCMHP) has reported drops in calls from women from 60 percent to 30 percent since lockdown, which is worrying. With men stuck at home, abused women are finding it difficult to make calls for help. GCMHP has responded by operating for longer hours, 12 hours a day, 7 days a week.
"Israel's threat of annexation didn't only kill whatever hope remained of the two-state solution, but it already psychologically paralysed the Palestinian Authority and compromised - along with the coronavirus - the Palestinian economy, most seriously in Gaza," Shehada explains.
"A large proportion of Gaza's economy is sustained through the salaries the PA sends to its tens of thousands of employees each month, but the PA hasn't been receiving its tax revenues from Israel since May, which made it unable to pay those salaries."
With the mental health crisis in Gaza continuing to grow, Shehada says a number of measures are needed to alleviate the suffering of Palestinians. Internally, Gazans need genuine unity between Hamas and Fatah and proper national elections so that people can elect a truly representative leadership.
Internationally, the global community needs to seriously challenge Israel and Egypt's blockade on Gaza, and demand that Israel assumes its responsibilities to an occupied population.
Shehada also suggests that the world community creates special scholarships for people from Gaza and create remote learning opportunities. "Through my calls with some of the youth in Gaza, they tell me that if Israel opens its crossings for hours, 30 percent will go out and migrate to other countries. This may lead to a decrease in the suicide rate in the future," says Eid.
Yousra Samir Imran is a British Egyptian writer and author who is based Yorkshire. She is the author of Hijab and Red Lipstick, being published by Hashtag Press in the UK in October 2020
Follow her on Twitter: @UNDERYOURABAYA


![President Pezeshkian has denounced Israel's attacks on Lebanon [Getty]](/sites/default/files/styles/image_684x385/public/2173482924.jpeg?h=a5f2f23a&itok=q3evVtko)



 Follow the Middle East's top stories in English at The New Arab on Google News
Follow the Middle East's top stories in English at The New Arab on Google News


